Pancreatic Stone or Kidney Stone? Pain in Abdomen – Still Unsure??
More than half the population in India assume they have kidney stones on encountering severe pain in the abdomen region.
It is so because in India, the chances of developing kidney stones are higher than having pancreatic stones.
In chronic pancreatitis, stones are detected in the pancreas, and the prevalence in India is 20-125 per 100,000 individuals.
Source: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5507364/
People suffering with pancreatic stones often have severe pain in the upper abdomen region, in kidney stones, the pain is in the lower abdomen region. This is the key difference between them and is one of the main pancreatic stone symptoms.
The symptoms of pancreatic stones are not to be ignored, and one must consult the best gastroenterologist for effective treatment of pancreatic stones.
Who should read this article:
- Individuals experiencing abdominal pain or related symptoms
- Patients already diagnosed with pancreatic stones
- People confusing pancreatic stones with kidney stones
- Anyone seeking awareness on the condition related to Pancreatic Stones
Location of the Pancreatic Stones
Pancreatic Stone Development Area 1
Pancreatic stones are developed in the main pancreatic duct, also known as Wirsung’s duct, and is the most common site of development.
The stones in the pancreas are formed due to the precipitation of calcium salts and protein plugs in the duct. These stones can block the flow of pancreatic juice which leads to increased pressure and pain.
Pancreatic Stone Development Area 2
The other region where the pancreatic stones develop is Branch (secondary) Pancreatic Ducts.
Here, smaller stones are developed in the side branches of the ductal system, which is usually observed in advanced stages, and in cases where the condition is long ignored.
Pancreatic Stone Development Area 3
The third region where the pancreatic stones are diagnosed is the Parenchyma of the Pancreas (pancreatic tissue itself).
In this condition, it is found rarely that the stones are embedded within the pancreatic tissue. This condition, if unchecked, may lead to structural damage, fibrosis, and can also cause dysfunction of the pancreas.
What most gastroenterologists worry about is the development of Chronic Pancreatitis. If the symptoms of pancreatic stones are not taken care of in time, it may lead to chronic pancreatitis.
In this condition, the ductal system is damaged due to repeated inflammation and the pancreatic juice composition is altered. Hence, it is important to consult the best gastroenterologist for pancreatic stone treatment once the pancreatic stone symptoms are identified.

Pancreatic Stone Symptoms
Pancreatic stones are a condition that can cause significant discomfort and disrupt the normal functioning of the pancreas.
These stones, often linked to chronic pancreatitis, form when substances like calcium carbonate solidify in the pancreatic ducts. Understanding pancreatic stone symptoms is crucial for timely diagnosis and treatment.
Common Symptoms of Pancreatic Stones
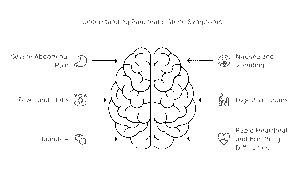
When pancreatic stones obstruct the ducts that connect the pancreas to the small intestine, they can lead to various symptoms. Here are some of the most common signs:
Severe Abdominal Pain
The most prominent symptom is intense pain in the upper abdomen. This pain may radiate to your back, chest, or even shoulders. It can be constant or intermittent, often worsening after meals.
Nausea and Vomiting
Many individuals experience nausea and vomiting during flare-ups caused by pancreatic stones. These symptoms can make eating and digestion difficult.
Fever and Chills
Fever accompanied by chills may occur due to inflammation or infection in the pancreas caused by the blockage.
Digestive Issues
Obstruction in the pancreatic ducts can lead to poor digestion, oily stools, or diarrhea due to insufficient enzyme flow into the intestines.
Jaundice
In rare cases, jaundice may develop, causing yellowing of the skin and eyes. This happens when bile flow is obstructed alongside the pancreatic ducts.
Rapid Heartbeat and Breathing Difficulties
Severe cases might lead to a fast heart rate (tachycardia) or shortness of breath due to complications like infection or inflammation.

