What is Achalasia Cardia?
Achalasia Cardia is a very uncommon disorder of swallowing which occurs in the esophagus, i.e., the pipe through which food goes from your mouth to your stomach. In this condition, the food and liquid cannot pass through the esophagus to the stomach because the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), a circular band of muscle at the bottom of the esophagus, fails to relax. The symptoms of Achalasia Cardia can make a person experience difficulty in swallowing, pain in the chest, heartburn, etc. For effective cure, consult the best gastroenterologist for Achalasia Cardia treatment.What are the causes of Achalasia Cardia condition?
The precise cause of Achalasia Cardia remains unclear, though it is suspected to be a result of the degeneration of nerves within the oesophagus, particularly the myenteric plexus. This degradation hinders proper signalling necessary for the relaxation of the lower oesophageal sphincter (LES) to open and pass food into the stomach. Possible causes of Achalasia Cardia are: Autoimmune Response: Several reports indicate that the immune system of the body may erroneously target the nerve cells in the oesophagus, causing them to degenerate. Genetic Factors: A genetic susceptibility may cause some individuals to be more prone to developing Achalasia. Infections: A few studies indicate viral infections, including those by the herpes simplex virus, as possible causes of the nerve damage causing Achalasia. Secondary Achalasia: Pseudo achalasia is also called secondary achalasia, which may be caused by other conditions like certain malignancies that target the oesophagus and the stomach. If you are suffering with symptoms of Achalasia Cardia, consult the best gastroenterologist for a proper diagnosis and treatment.
What are the Symptoms of Achalasia Cardia?
Achalasia Cardia usually targets the oesophagus and the passage of food and fluids into the stomach. The key symptoms of Achalasia Cardia are listed below: Difficulty in swallowing (dysphagia): Most frequent symptom, difficulty in solid and liquid food intake. Regurgitation: Return of undigested food and saliva to the mouth. Chest pain: Characterized as a pressure or tightness, occasionally mistaken for cardiac conditions. Weight loss: Resulting from difficulty in swallowing and regurgitation, followed by malnutrition. Heartburn: Rare, but it resembles the symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Choking or Coughing: Particularly with or after taking meals. If you are experiencing symptoms of Achalasia Cardia, consult the best gastroenterologist for effective treatment.What is the Diagnosis of Achalasia Cardia?
Achalasia Cardia causes a great amount of discomfort to the patient, and for effective treatment, a proper diagnosis is required. To confirm Achalasia Cardia, gastroenterologist advice for these diagnosis tests: Endoscopy: A very thin, bendable tube equipped with a video camera is guided through the mouth into the stomach and oesophagus. Using this, the physician can examine the oesophagus visually and exclude other disease conditions. Esophageal Manometry: This examination records the rhythmic contractions of the muscles (peristalsis) of the esophagus and the functioning of the LES. It assists in ascertaining whether the LES is relaxing in a normal fashion during swallowing.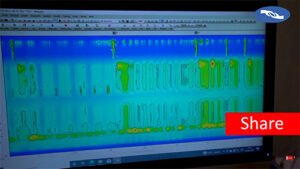 Barium Swallow: X-ray examination where the patient swallows a barium solution that coats the esophagus. This enables the physician to observe the shape and movement of the esophagus and detect narrowing or obstruction. These examinations assist in precisely diagnosing Achalasia Cardia. If you have symptoms of Achalasia Cardia, consulting the best gastroenterologist would be a wise decision.
Barium Swallow: X-ray examination where the patient swallows a barium solution that coats the esophagus. This enables the physician to observe the shape and movement of the esophagus and detect narrowing or obstruction. These examinations assist in precisely diagnosing Achalasia Cardia. If you have symptoms of Achalasia Cardia, consulting the best gastroenterologist would be a wise decision. Treatment of Achalasia Cardia
Achalasia Cardia treatment involves relieving symptoms and facilitating the entry of food into the stomach. Most Gastroenterologists opt for Balloon Dilation (Pneumatic Dilation), Heller Myotomy, Botulinum Toxin (Botox) Injections, and Medications, including Lifestyle and Dietary changes, to treat Achalasia Cardia. However, the most preferred method is Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy (POEM) to treat Achalasia Cardia.Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy (POEM)
 Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy (POEM) is a minimal invasive endoscopic treatment for Achalasia Cardia. POEM is a new technique where a tiny cut is made in the inner mucosa of the esophagus to incise the muscle layers, thus relaxing the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) and enhancing the delivery of food into the stomach.
Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy (POEM) is a minimal invasive endoscopic treatment for Achalasia Cardia. POEM is a new technique where a tiny cut is made in the inner mucosa of the esophagus to incise the muscle layers, thus relaxing the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) and enhancing the delivery of food into the stomach. Procedure Overview
Preparation: The patient receives a pre-anesthesia checkup for confirmation that the patient is suitable for the procedure. Antibiotic prophylaxis is given to avoid infection. Endoscopic Access: An endoscope, which is a camera-equipped flexible tube, is introduced through the mouth into the esophagus. Mucosal Incision: An incision is made in the mucosa (inner lining) of the esophagus. Submucosal Tunnel: A tunnel in the submucosal layer is created to access the muscle layers. Myotomy: Muscle fibres of the LES are incised to unblock the obstruction. Closure: The mucosal cut is closed with endoscopic clips or sutures.Benefits
Minimally Invasive: Less invasive, resulting in faster recovery and less discomfort. Effective: It offers long-term relief of symptoms in more than 90% of patients. Shorter Hospital Stay: Patients recover more quickly than with conventional surgery. Post-Operative Care:- Patients are usually kept in the hospital for 2-3 days for monitoring.
- A liquid or soft diet is recommended initially, gradually transitioning to regular foods.
- Follow-up appointments and tests may be scheduled to assess the effectiveness of the procedure.
Achalasia Cardia is a rare esophageal disorder where the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) fails to relax, making it difficult for food and liquids to reach the stomach.
The exact cause is unclear, but it may result from nerve degeneration, autoimmune responses, genetic factors, or viral infections.
Common symptoms include difficulty swallowing (dysphagia), chest pain, regurgitation, weight loss, and nighttime choking.
Diagnosis involves tests like endoscopy, esophageal manometry, and barium swallow X-rays to evaluate esophageal function.
Yes, treatment options include POEM (Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy), balloon dilation, Heller myotomy, Botox injections, and medication.